Question 8:What are conjugated bonds?
Answer.
Question 9. Why are alkanes more reactive than alkyne?
Answer.
Answer.
Alternated sigma and pi bonds are called conjugated bonds.
Conjugated bonds are only formed if
1. two pi bonds are separated by a single sigma bond and
2.all adjacent p orbitals are aligned (co-plainer) with each other.
On the other hand, conjugated bonds are not formed if there are two or more sigma bonds between two pi bonds or p orbitals of adjacent pi bonds are not co-plainer.
In conjugated bonds, pi bonds are close enough to each other to interact across sigma bonds. Due to interaction between two pi bonds, a partial double bond is formed which enables the pi electrons to be delocalized over whole system.
Conjugated bonds are only formed if
1. two pi bonds are separated by a single sigma bond and
2.all adjacent p orbitals are aligned (co-plainer) with each other.
On the other hand, conjugated bonds are not formed if there are two or more sigma bonds between two pi bonds or p orbitals of adjacent pi bonds are not co-plainer.
In conjugated bonds, pi bonds are close enough to each other to interact across sigma bonds. Due to interaction between two pi bonds, a partial double bond is formed which enables the pi electrons to be delocalized over whole system.
Question 9. Why are alkanes more reactive than alkyne?
Answer.
Although electron density in alkyne is higher than in alkene, still alkyne are less reactive in electrophilic additions. There are two reason for low reactivity of alkyne.
1. Electronegativity of sp hybridized carbon atoms of triple bond in alkynes is higher than that of sp2 hybridized carbon atoms of double bond in alkenes. As a result, pi electrons of alkyne are tightly held and not easily available for electrophilic addition reactions. Thus alkynes are less reactive.
2. Due to sp hybridization, carbon - carbon bond length is shorter in alkyne. Hence, unhybridized p orbitals effectively overlap with each other and bond strength is increased. It also makes alkynes less reactive.
3. Due to attack of an electrophile on alkyne, vinyl cation is formed as an intermediate which is relatively unstable than alky cation formed in case of alkenes. It also decreases the reactivity of alkyne.
1. Electronegativity of sp hybridized carbon atoms of triple bond in alkynes is higher than that of sp2 hybridized carbon atoms of double bond in alkenes. As a result, pi electrons of alkyne are tightly held and not easily available for electrophilic addition reactions. Thus alkynes are less reactive.
2. Due to sp hybridization, carbon - carbon bond length is shorter in alkyne. Hence, unhybridized p orbitals effectively overlap with each other and bond strength is increased. It also makes alkynes less reactive.
3. Due to attack of an electrophile on alkyne, vinyl cation is formed as an intermediate which is relatively unstable than alky cation formed in case of alkenes. It also decreases the reactivity of alkyne.
Question 10. Justify the given order of reactivity? Alkenes >alkyne>alkyne.
Answer.
Answer.
Both alkenes and alkyne are more reactive than alkanes due to following reasons.
1. Both alkene and alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons and contain pi bonds which are relatively easier to break than sigma bonds present in Alkane.
2. Both alkenes and alkynes have higher electron density on unsaturated bond than alkanes, due to which both readily undergo electrophilic addition reaction.
Question 11. What is meant by dehydration reaction of alcohol?
Answer.
A reaction in which a molecule of water is removed from alcohol is called dehydration. Dehydration reaction can be performed by heating alcohol with either protic acid (H2SO4 or H3PO4), P4O10 or Al2O3 etc.
Example
Previous
1. Both alkene and alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons and contain pi bonds which are relatively easier to break than sigma bonds present in Alkane.
2. Both alkenes and alkynes have higher electron density on unsaturated bond than alkanes, due to which both readily undergo electrophilic addition reaction.
Question 11. What is meant by dehydration reaction of alcohol?
Answer.
A reaction in which a molecule of water is removed from alcohol is called dehydration. Dehydration reaction can be performed by heating alcohol with either protic acid (H2SO4 or H3PO4), P4O10 or Al2O3 etc.
Example
Question 12. What are polymerization reactions?
Answer: A reaction in which several small molecules (monomers) combine together to form a larger or macromolecule is called polymerization. Such macromolecules are called polymers.
Example
Question 14: What is resonance energy?
Answer.
Resonance energy can be defined as '' the difference of energy between actual molecule with delocalized electrons and and most stable contributing structure with localized electrons is called resonance energy.
Simply, it is difference between energy of molecule due to localized bond and energy lost due to delocalized bonds.
For example, the energy difference between actual benzene and most stable cyclohexatriene is 152 kj/mole. Thus, benzene is 152 kj/mole more stable than it most stable canonical structure.
Example
Question 13. What is resonance?
Answer.
The process in which delocalized electrons in a molecule or ion are represented by a set of several Lewis structures instead of a single Lewis structure is called resonance. These several structures of a molecule or ion are called resonance structures or canonical structures.
Actual structure of a molecule which can describe the whole properties of a molecule cannot be drawn. However, actual structure is considered to be a resonance hybrid of all possible contributing structures.
The process in which delocalized electrons in a molecule or ion are represented by a set of several Lewis structures instead of a single Lewis structure is called resonance. These several structures of a molecule or ion are called resonance structures or canonical structures.
Actual structure of a molecule which can describe the whole properties of a molecule cannot be drawn. However, actual structure is considered to be a resonance hybrid of all possible contributing structures.
Question 14: What is resonance energy?
Answer.
Resonance energy can be defined as '' the difference of energy between actual molecule with delocalized electrons and and most stable contributing structure with localized electrons is called resonance energy.
Simply, it is difference between energy of molecule due to localized bond and energy lost due to delocalized bonds.
For example, the energy difference between actual benzene and most stable cyclohexatriene is 152 kj/mole. Thus, benzene is 152 kj/mole more stable than it most stable canonical structure.
Previous

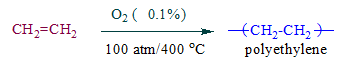
Comments
Post a Comment