Question. Sketch the molecular orbital pictures of π (2px) and π (2px∗).
Answer.
Question. Explain the valence bond theory qualitatively.
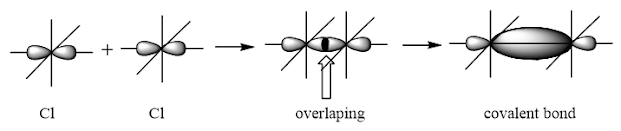
Answer. According to this theory, a covalent bond is formed when Half filled atomic orbital of one atom overlaps with half filled atomic orbital of another atom. As a result of overlap, the electrons with opposite spins become paired (according to Pauli’s exclusion principle) to stabilized themselves. Greater the overlap, the stronger the bond. The direction of bond is determined by the direction of two overlapping orbital’s.
Question. How the bonding in the following molecules can be explained with respect to valence bond theory? Cl2, O2, N2, HF, H2S.
Answer.
Cl2
Valence electronic configuration of Cl
The basic requirement for bond formation is that the overlapping orbitals must be partially filled. As one p orbital of Cl atom is partially filled, so it will take part in bond formation with other p orbital of an other Cl atom and will acquired the shared pair of electrons.
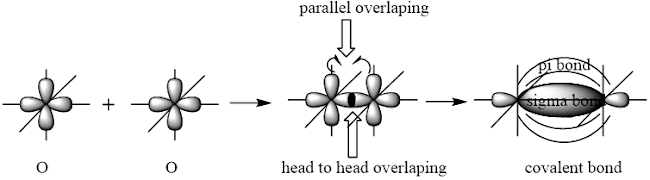
O2
Valence electronic configuration of O
The basic requirement for bond formation is that the overlapping orbitals must be partially filled. As two p orbitals of of O atom are partially filled, so it will take part in bond formation with other p orbitals of other O atom and will acquired the shared pair of electrons. One head to head overlap occurs to give a sigma bond and other parallel overlap causes a pi bond.
N2
Valence electronic configuration of N
7N = 2s, 2px, 2py, 2pz The basic requirement for bond formation is that the overlapping orbitals must be partially filled. As three p orbitals of of N atom are partially filled, so they will take part in bond formation with other p orbitals of other N atom and will acquired the shared pair of electrons. One head to head overlap occurs to give a sigma bond and other two parallel overlaps give two pi bonds.
HF
Valance shell electronic configuration of H and F
H: 1S F: 2S, 2px,2py, 2pz The basic requirement for bond formation is that the overlapping orbitals must be partially filled. As one orbital of F atom is partially filled, so it will take part in bond formation with partially filled s orbital of H atom and will acquired the shared pair of electrons.
H2S
Valance shell electronic configuration of H and S
The basic requirement for bond formation is that the overlapping orbitals must be partially filled. As two p orbitals of of S atom are partially filled, so they will take part in bond formation with s orbitals of H atom and will acquired the shared pair of electrons.
Hybridization
Question. What is meant by atomic hybridization?
Answer. The process by which atomic orbitals of slight energy difference, intermix with each other in an atom to form a new set of equivalent orbitals, which have same energies and shapes is called hybridization. The number of intermixing orbitals are equal to hybridized orbitals.
Question. Why concept of hybridization has been introduced?
Answer. The idea of hybridization has been introduced for explaining the equivalent tetra-valency of carbon and bond angles in H2O and NH3 molecule.
Question. Explain atomic orbital hybridization with reference to sp3, sp2 and sp modes of hybridization for PH3, C2H4, C2H2.
Answer.
SP3 Hybridization: The process in which one s and three p atomic orbitals intermix with each other to form four equivalent sp3 hybrid orbitals, is called sp3 hybridization. For example PH3: To understand the sp3 hybridization of P in PH3, we should know the electronic configuration of 15P.
One s and three p orbitals intermix to form four sp3 hybrid atomic orbitals. They are directed towards the four corners of a tetrahedron because in this geometry repulsion between orbitals is minimum. Geometry of the molecule is pyramidal because at there as a lone pair of electron in one of sp3 orbital.
SP2 Hybridization: The process in which one s and two p atomic orbitals intermix with each other to form three equivalent sp2 hybrid atomic orbitals, is called sp2 hybridization. For example CH2 = CH2: To unde
One s and three p orbitals of P intermixe to form three sp3 hybrid atomic orbital. They are directed towards the three corners of a trigonal because in this geometry repulsion between orbitals is minimum. Geometry of the molecule is trigonal with a one electron in one p orbital.
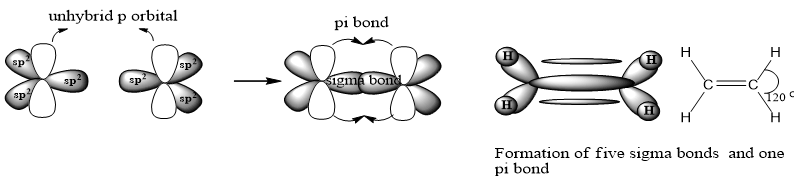
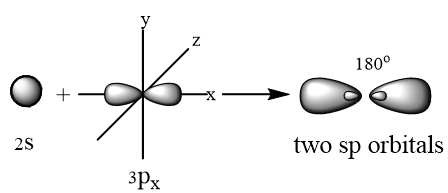
SP Hybridization: The process in which one s and one p atomic orbitals intermix with each other to form two equivalent sp hybrid atomic orbitals, is called sp hybridization. For example CH≡ CH: To understand the sp2 hybridization of C in CH≡ CH, we should know the electronic configuration of 6C.
One s and one p orbital of p intermixes to form two sp hybrid atomic orbital. They are directed at angle of 180 because in this geometry repulsion between orbitals is minimum. Geometry of the molecule is linear with two unpaired electrons in two unhybrid orbitals.









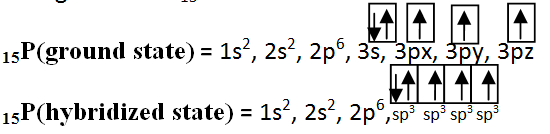






Comments
Post a Comment