Stoichiometry, Limiting-reactant-excess-reactant, Different mass -same molecules, limiting-reactant-theoretical-yield-actual-yield-molar-volume
Question 1. 58.5 a m u are termed as formula mass and not molecular mass of NaCl. Why?
Answer.
As NaCl is an ionic compound and doesn't exist in molecular form. So 58.5 amu is termed as formula mass rather than molecular mass.
Question 2. Concept of limiting reactant is not applicable to the reversible reactions. Explain.
Answer.
As limiting reactant is the reactant that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction while in reversible reaction none of reactant is completely consumed. Therefore, the concept of limiting reactant is not applicable to the reversible reaction.
Question 3. How many covalent bonds are present in 9 gram of water?
Answer.
Mass of water (H2O) = 9g
Molar mass of H2O = 18g/mole
Number of moles of H2O = ?
= 3.011 × 1023
1 molecule of H2O contains = 2 covalent bonds
3.011 × 1023 molecules of H2O contain = 2 x 3.011 × 1023 = 6.022 × 1023 covalent bonds
Answer. One mole of different compounds have have different masses but same number of molecules. Reason is that molecules of different compounds have different molecular masses. Therefore, their molar masses are also different. Hence, one of mole of different have different masses although same number of molecules.
Example
Molecular mass of H2O = 18 amu
Molar mass of H2O and = 18 g
1 mole of H2O = 18 g
Molecular mass of CO2 = 44 amu
Molar mass of CO2 and = 44 g
1 mole of CO2 = 44 g
Question 8: 23 g of sodium and 238 g of urinum have same number of atoms.
Answer.
Mass of sodium = 23 g
Molar mass of sodium = 23 g/mole
No. of moles of sodium = 23 g/ 23 g/mole = 1 mole
Mass of urinum = 238 g
Molar mass of urinum = 238 g/mole
No. of moles of sodium = 238 g/ 238 g/mole = 1 mole
Hence,
No. of moles of Na = No. of moles of U
So, both have same number of atoms.
Question 9. Calculate the weight of oxygen gas evolved when 5 gram of KClO3 are completely decomposed thermally.
Answer.
Given mass of KClO3 = 5 g
Molar mass of KClO3 = 39 +35.5 +16 × 3 = 122.9 g/mole
No. of moles of KClO3 = (5 /122.5) = 0.0406 moles
According to balanced chemical reaction
2 moles of KClO3 = 3 moles of O2
1 mole of KClO3 = 3/2
0.0408 moles of KClO3= (3/2) × 0.0408
= 0.0612moles
Mass of KClO3 = No. of moles of KClO3 × Molar mass of KClO3
= 0.0612 moles × 32 g/mole
= 1.958 g
Question 10. What is the relationship between mass and volume of a gas at STP?
Answer
The volume occupied by 1 mole of gas at STP is called molar volume. Its numerical value is 22.414 dm3. Mass of 1 mole of a gas is called its molar mass. So, molar mass of a gas occupies 22.414 dm3 at S. T. P.
e. g.
Mass of 22.414 dm3 of CO2 at S. T. P. = 44 g
Mass of 22.414 dm3 of N2 at S. T. P. = 28 g
Question 11. The actual yield is less than theoretical yield. Give reasons
Answer.
Actual yield it is always less than practical due to following reasons.
1. Formation of by product due to side reaction
2. Incomplete reactions due to some of reactants which do not react completely
3.Reversible reactions may occur.
4. Mechanical loss due to filtration, distillation, separation by separating funnel washing and crystallization etc.
Question 12. What are representative particles in one mole of a gas at STP?
Answer. One mole of any gas at STP has a volume of 22.414 dm3
and contains 6.022 × 1023 representative particles of that gas.
For example,
1 mole of CO2 has volume of 22.414 dm3 and contains 6.022 × 1023molecules
1 mole of N2 has volume of 22.414 dm3 and contains 6.022 × 1023molecules
Question 13. What is stoichiometry and stoichiometric amounts?
Answer
The branch of chemistry which deals with study of relative amount of substances involved in a chemical reaction has given a balanced chemical equation is called stoichiometry.
The amount of reactants according to balance chemical equation are called dichromatic amounts.

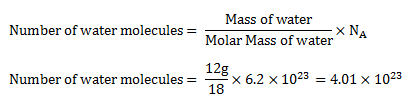

Informative..
ReplyDeleteNice of sir